Railway Safety Standards: An Overview
Railway safety is a critical aspect of transportation that ensures the protection of passengers, staff, and infrastructure. Adhering to established safety norms is essential for minimizing risks and enhancing the reliability of railway systems. This blog post will explore key European railway safety standards EN 50126, EN 50128, and EN 50129.
Safety measures are essential not only for protecting passengers and staff from equipment malfunctions but also help to ensure that systems safely respond in the situation of security attacks, such as attacks on the availability of components (fail-safe).
EN 50126: The RAMS Lifecycle
EN 50126 defines the RAMS (Reliability, Availability, Maintainability, and Safety) life cycle for railway applications.
The standard describes the phases of the lifecycle from the concept phase to the decommissioning of the system and addresses system issues on the scale of the whole railway system.
Besides defining the life cycle, EN 50126-1 defines requirements regarding organization, verification and validation, Independant Safety Assessment.
In EN 50126-2, the safety process including the risk assessment and apportionment of the Safety Integrity Requirements is defined, as well as requirements for the design, implementation, demonstration, and acceptance of the system.
EN 50128: Software for railway control and protection systems
As railway systems increasingly rely on software, EN 50128 addresses methods and processes for software development to meet the demands for safety. The standard does not define how to decide which SIL (Safety Integrity Level) is required. The processes to define the safety functions allocated to software are specified by EN 50126 and EN 50129.
EN 50129: Safety related electronic systems for signalling
EN 50129 has to goal to enable cross-acceptance of Safety Approvals for generic products and generic applications, which are then to be used for different specific applications, in different countries.
EN 50129 is based on the lifecycle described in EN 50126.
It’s main requirements deal with the structure and content of the Safety Case and the System Safety Acceptance process.
Relationship to EN 61508
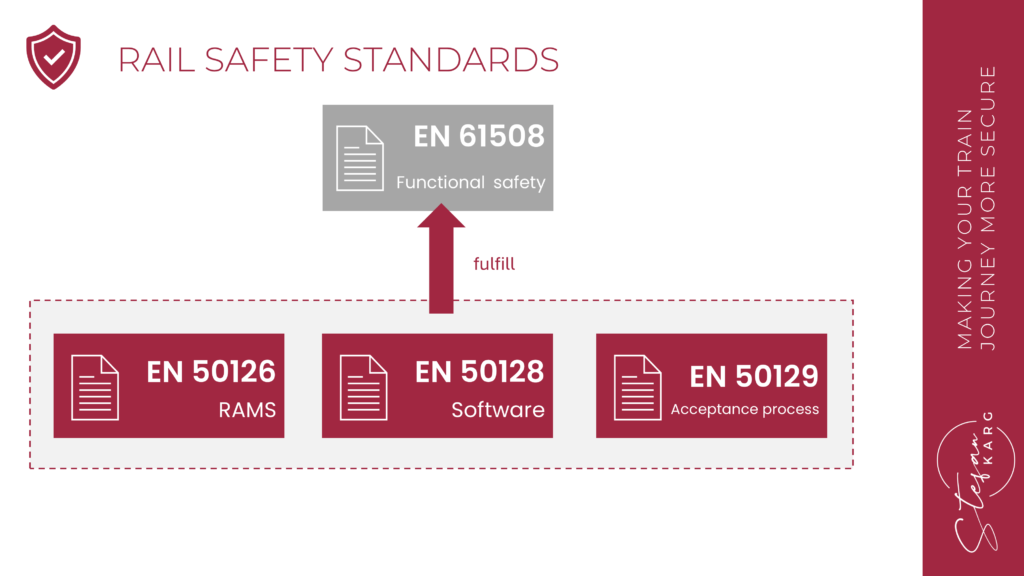
The standards EN 50126, EN 50128 and EN 50129 combined are the railway equivalent of EN 61508, which is the generic, non-railway specific, standard for functional safety. If you are able to demonstrate compliance with those three railway specific standards, a further evaluation of EN 61508 is not required.
Transparency notice: I used Atlassian AI and DeepL Write to support me while writing this article.